Research Background
The Paris Agreement established a long-term global goal for climate change mitigation, which is to limit the increase in global average temperature to 2 °C above pre-industrial levels while pursuing efforts to limit the increase even further to 1.5 °C. Studies have found that if scenarios were designed to keep global warming within 1.5 °C, the world would need to reach net zero emissions between 2050 and 2060; to achieve the 2 °C goal, it would need to reach net zero emissions after 2070. On September 22, 2020, President Xi Jinping announced at the General Debate of the 75th session of the UN General Assembly that China would enhance nationally determined contributions, adopt more vigorous policies and initiatives, strive to peak CO2 emissions by 2030, and achieve carbon neutrality by 2060.
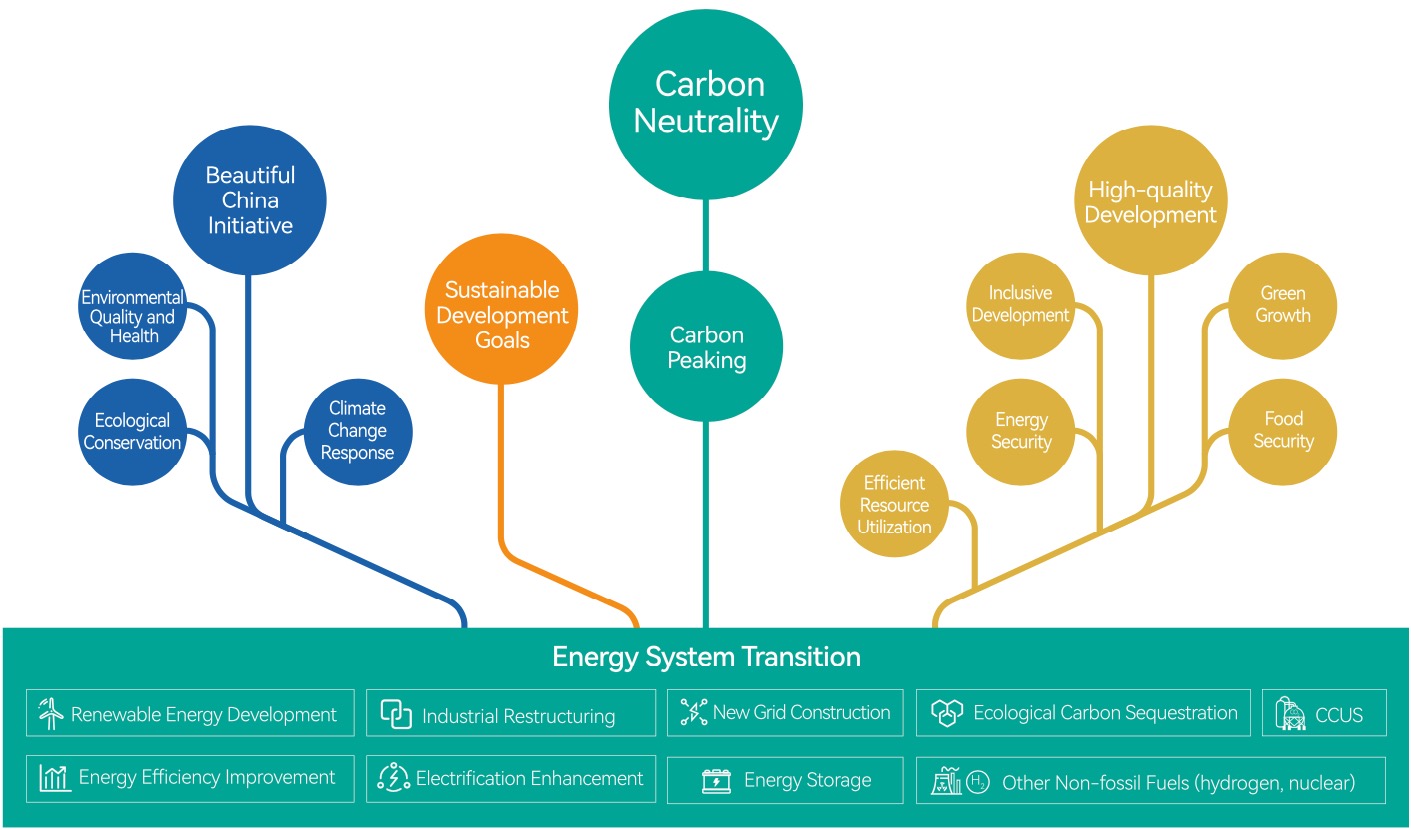
Energy-related activities are the primary source of carbon emissions, implying that a low-carbon transition of the energy system is not only necessary but also urgent; it is not only a transformation of the energy system but also a systemically socioeconomic change. The low-carbon energy system transition is the key to promoting the ""dual carbon” goals, an important way to catalyze green growth, facilitate the harmonious coexistence between human and nature, and build a beautiful China.
2035 is a year with special significance. Looking ahead to 2035, China will broadly achieve socialist modernization and the Beautiful China Initiative. Vision 2035 determines whether China can achieve two important international commitments by 2030, namely the carbon peaking target and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) set in the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. If China successfully achieves the carbon peaking goal by 2030, there would only be around 30 years left for China to proceed from carbon peaking to carbon neutrality, and the preliminary trajectory of carbon neutrality will be given in 2035 after carbon peaking.
Research Methods
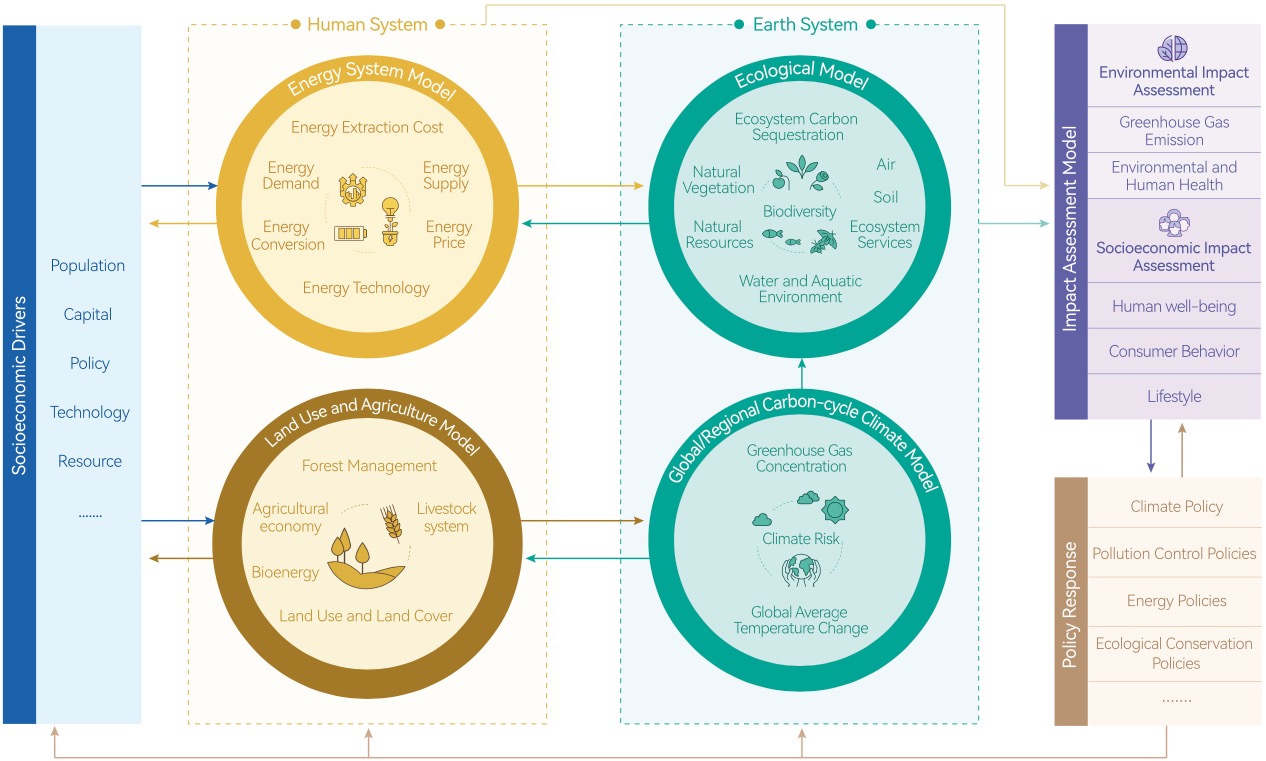
CEMF03 studies the pathways and corresponding policies under multiple scenarios of low-carbon development and the Beautiful China 2035 vision through integrated assessment modeling. The study is based on five research modules: socioeconomic drivers, human system, earth system, impact assessment model and policy response. In addition, the three modules – human system, earth system, and impact assessment model – conduct in-depth research on their sub-topics (i.e., energy, agriculture, ecology, climate, and environment) based on different models, simulating the impact of various strategies on SDGs and climate change to guide the direction for policy responses. Meanwhile, different types of models in each module are coupled using Multi-sector Dynamics Modeling to further analyze inter-module interactions, dynamic feedback, and synergies. Applying this method, CEMF03 explores the pathways and strategic measures for sustainable development and climate change response in various sectors systematically and comprehensively. Moreover, it provides a new way of thinking for achieving climate goals and SDGs while minimizing potential trade-offs and maximizing synergies among all modules.
Research Objectives
China Energy Modeling Forum’s (CEMF) third theme study, CEMF03, focuses on "2035 Low-Carbon Development and Beautiful China". It conducts cross-sectoral systemic modeling research on energy, economy, and environment, with a core mission to promote low-carbon energy transition, green growth, and sustainable development. One goal of the study is to maximize the overall benefits to society, the economy, the environment, and health, while the other is to foster the synergistic development of multiple objectives. CEMF03 aims to link the “Beautiful China 2035” goal with global climate, environment, and sustainable development goals to provide strong scientific support for industrial restructuring, pollution control, ecological conservation, climate change response, and the concerted promotion of carbon reduction, pollution reduction, green expansion and economic growth.
Integrated Assessment Modeling Framework for Climate Change